Even as the fate of the inland portions of the Nationwide Differential GPS (NDGPS) reference network hangs in the balance, the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) has awarded a contract to Trimble for up to 400 high-accuracy GPS reference receivers.
The Trimble NetRS reference receivers will be installed over the next three years as part of the coast guard’s modernization of the Maritime DGPS Service, which is not part of the NDGPS elements that being considered for termination.
Even as the fate of the inland portions of the Nationwide Differential GPS (NDGPS) reference network hangs in the balance, the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) has awarded a contract to Trimble for up to 400 high-accuracy GPS reference receivers.
The Trimble NetRS reference receivers will be installed over the next three years as part of the coast guard’s modernization of the Maritime DGPS Service, which is not part of the NDGPS elements that being considered for termination.
By January 30, 2008, the U.S. Department of Transportation (DoT) is scheduled to complete its assessment of the need for an inland component of NDGPS, according to Tim Klein, senior policy advisor/NDGPS Coordinator for DoT’s Research and Innovative Technology Administration (RITA).
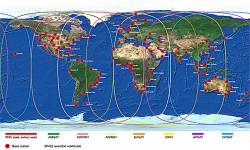
NDGPS is an expansion of a maritime system the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) begun in the late 1980s, which uses low-frequency radiobeacon transmissions to communicate real-time differential corrections and integrity messages. User communities include farmers, public utilities, marine navigators, and geographic information system (GIS) developers.
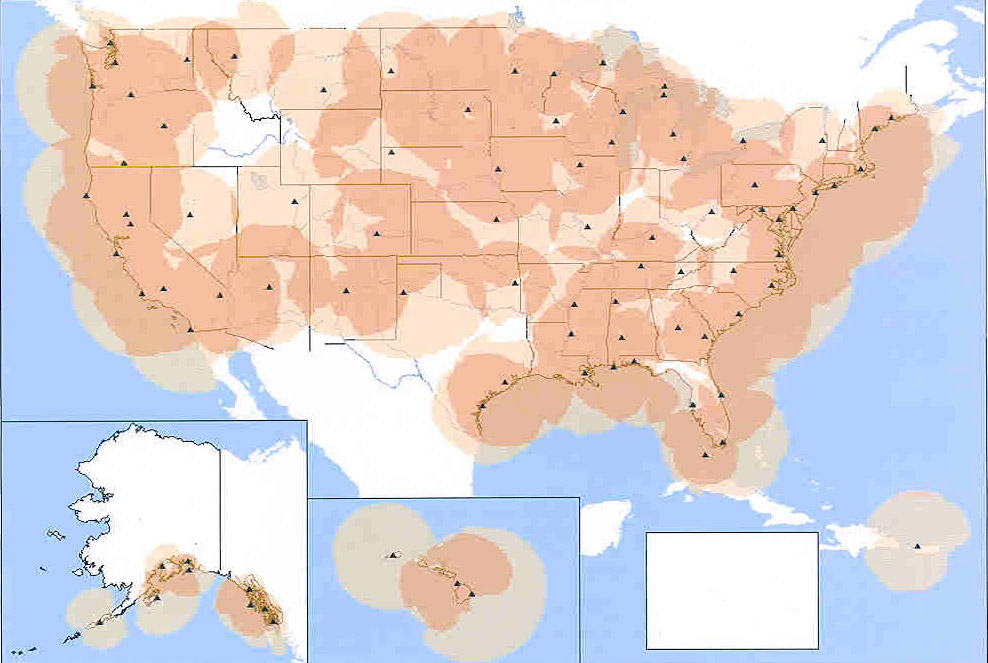
Operated by the USCG Navigation Center (NAVCEN), the Maritime DGPS Service consists of two control centers and more 85 remote broadcast sites. The service broadcasts correction signals on marine radiobeacon frequencies to improve the accuracy and integrity of GPS-derived positions. The service’s requirement is to provide 10-meter real-time accuracy, but typically delivers accuracies of 1-3 meters in all established coverage areas.
NetRS receivers have 24 channels capable of receiving the GPS L1 C/A code, the new L2 civil signal (L2C), full-cycle carriers on L1/L2, and space-based augmentation signals. The survey receivers incorporate the Trimble Maxwell custom GPS Chip.
Previously, as part of the modernization project, the USCG had purchased 400 Trimble Zephyr Geodetic antennas along with Trimble Charisma software, which provides the backbone of the DGPS radiobeacon operating architecture.
As for the NDGPS program as a whole, the system currently has 86 operational sites established over the past 10 years — 8 sites short of complete coverage of the contiguous 48 United States.
Fiscal Year 2008 (FY08) funding for NDGPS is $5 million, which can be used only for operations and maintenance (O&M) of the existing system; no construction, expansion, or upgrade for NDGPS sites in FY 07/08. RITA agreed to be the interim program sponsor.
If neither transportation requirements nor other federal user requirements appear during its investigation, DoT intends to develop a decommissioning plan for NDGPS.
The FY09 USCG resource proposal requests O&M funding to maintain maritime DGPS. No matter what the outcome for inland NDGPS, USCG will continue to maintain maritime DGPS, Klein says.
Copyright © 2007 Gibbons Media & Research LLC, all rights reserved.